Diferencia entre revisiones de «DL-Fosfinotricina»
La enciclopedia de ciencias y tecnologías en Argentina
(inicial) |
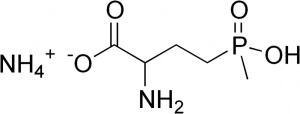
(Estructura 2D de la DL-Fosfinotricina.) |
||
| Línea 1: | Línea 1: | ||
| + | [[Archivo:DL-Fosfinotricina.jpg|300px|right|thumb|<small><center>'''Estructura 2D de la DL-Fosfinotricina.'''</center></small>]] | ||
'''DL-Fosfinotricina''' is a herbicide commonly used in plant molecular biology and plant tissue culture. It is the ammonium salt of glufosinate. It is also known as glufosinate ammonium. | '''DL-Fosfinotricina''' is a herbicide commonly used in plant molecular biology and plant tissue culture. It is the ammonium salt of glufosinate. It is also known as glufosinate ammonium. | ||
The herbicide is a broad spectrum herbicide which is comparatively biodegradable, similar to glyphosate.[1] Glyphosate was first sold by Monsanto Company under the tradename Roundup, but is no longer under patent. Glufosinate is sold under trade names Basta, Buster and Liberty. Crops have been developed (genetically engineered) which are resistant to this herbicide through the insertion of the bar gene[2] into plants. | The herbicide is a broad spectrum herbicide which is comparatively biodegradable, similar to glyphosate.[1] Glyphosate was first sold by Monsanto Company under the tradename Roundup, but is no longer under patent. Glufosinate is sold under trade names Basta, Buster and Liberty. Crops have been developed (genetically engineered) which are resistant to this herbicide through the insertion of the bar gene[2] into plants. | ||
Revisión del 20:07 9 sep 2012
DL-Fosfinotricina is a herbicide commonly used in plant molecular biology and plant tissue culture. It is the ammonium salt of glufosinate. It is also known as glufosinate ammonium. The herbicide is a broad spectrum herbicide which is comparatively biodegradable, similar to glyphosate.[1] Glyphosate was first sold by Monsanto Company under the tradename Roundup, but is no longer under patent. Glufosinate is sold under trade names Basta, Buster and Liberty. Crops have been developed (genetically engineered) which are resistant to this herbicide through the insertion of the bar gene[2] into plants.